· Strategic Advantage Profile(SAP)
The strategic advantage profile is a tool for making
a systematic evaluation of the enterprises internal factors which are
significant for the company in its environment. The SAP shows the strengths and
weakness of an organization in different functional areas.
The inherent potential
of a firm to take advantage of its strengths and overcome its weakness, in
order to avail the opportunities provided and face the threats that are given
by the external environment, this capacity factor of an organization is called
the corporate capability factors, strategic factors, strategic advantage
factors and corporate competence factors. Strategic advantages are the outcome
of organizational capabilities. The result of these organizational activities
leads to rewards in terms of financial parameters such as profit or shareholder
value and non financial rewards such as market share or reputation. On the
other hand the penalties in the form of market share loss or financial loss is
called the strategic disadvantages. Strategic advantages can be measured by
using the parameters in which they are expressed like higher the profitability
better is the strategic advantage. Within the internal environment of an
organization different types of capability factors exists, these capability
factors of an organization are divided into different functional areas such as
Financial, Marketing, Operations, Personnel, Information Management and General
Management of the organization
The
strategist should look to see if the firm is stronger in these factors than its
competitors. When a firm is strong in the market, it has a strategic advantage
in launching new products or services & increasing market share of present
products & services. There are generally 5 functional areas in most of the
organizations. These areas are:-
✓ Marketing and
Distribution
✓ R & D and
Engineering
✓ Production and
Operations management
✓ Corporate resources
and personnel
✓ Finance and Accounting
1]
Strategic advantage factors: Marketing and Distribution
1.
Efficient and effective market research system
2.
The product service mix: quality of product and service and service
3.
Strong new - product and new- service leadership
4.
Patent protection (or equivalent legal protection for life)
5.
Positive feeling about the firm and its products and services on the part of
the ultimate consumer
6.
Efficient and effective packaging of products (or the equivalent for service)
7.
Effective pricing strategy for products and services
8.
Efficient and effective marketing promotion activities other than advertising
9.
Efficient and effective service after purchase
10.
Efficient and effective channel of distribution and geographical coverage,
including internal efforts.
2]
Strategic advantage factors: R & D and Engineering
1.
Basic research capabilities within the firm
2.
Excellence in product design
3.
Excellence in process design and improvement
4.
Superior packaging development being created
5.
Improvement in the use of old or new materials
6.
Ability to meet design goals and customer requirements
7.
Trained and experienced technicians and scientists
8.
Work environment suited to creativity and innovation
9.
Well – equipped laboratories and testing facilities
3]
Production and Operations management [ for 3, 4 & 5 refer OCP]
4]
Corporate resources and personnel
5]
Finance and Accounting
A
picture of the more critical areas which can have a relationship of the
strategic posture of the firm in the future.
PROFILE
OF SAP
A
concise chart of strategic advantage profile is prepared on the basis of
detailed information presented in the functional area profile. The strategic
advantage profile is a tool for making a systematic evaluation of the
enterprises internal factors which are significant for the company in its
environment. The SAP shows the strengths and weakness of an organization in
different functional areas.
Difference between the OCP &
SAP
The
outcome of the organizational capabilities is the strategic advantage. These
outcome of organizational capabilities are measured in terms of financial
parameters such as profit or shareholder’s value and non- financial parameters
like market share and reputation. On the other hand the disadvantages in the
form of loss and damage to market share are categorized into strategic
disadvantages. By using the parameters in which they are expressed, strategic
advantage are expressed in absolute terms like higher the profitability better
is strategic advantage of an organization. In order to compare the strategic
advantage over a period of time, an organization’s performance over a period of
time and its current performance with respect to its competitors in the
industry are used. So competitive advantage is a special case of strategic
advantage where the rewards or penalties could be measured against one or more
identified rivals in the industry. Thus the competitive advantage could be to
outperform its rivals in profitability or market standing. Competitive
advantage is measured and compared with respect to the competitors in the
industry so competitive advantage is a relative term rather than absolute. So
we can conclude that strategic advantage is a broader concept while competitive
advantage is one of its subset and strategic advantage is measured in absolute
term whereas competitive advantage in broader terms.
· BCG growth –Share matrix
BCG
Matrix is a matrix of Growth rate of the industry and Market share.
·
Growth
rate of the industry
-
Percentage
(%) of increase in sales
·
Market
share
-
Relative
market share of a firm = Market share in industry/market share of the largest
other competitor
i.
>
1 indicates market leader
Assumption
: Other things equal - growing market is attractive
Line
separating high & low competition position set at 1.5 times (needed to have
dominant position & to be called as star/cash cow),
A
product is indicated by circle; Area of circle significance to company - in
terms of assets used/sales
Similar
to product life cycle
Star
-
Market leader, peak of product life cycle, enough cash to maintain high share
(market), Growth rate slow
-
Becomes cash cows, More resources
-
Investment to support high growth No immediate profits
-
Great potential
-
Future Medium risk category
Question Marks - (Problem children/wild cats)
-
New products with potential for success
-
More resources but future uncertain
-
high risk category Money taken from mature products & spent on ? Slow
growth dogs
Cash cows
-
more money than needed for maintaining market share
-
Declining stage of life cycle Cash milked from for investment in ? Higher
profit
Dogs
-
Weak market share, low growth market cash trap of the company Identify Issues
-
current position & future position without change in the strategy
Goal
The goal
of BCG analysis is help firms to have a balanced portfolio
-
Maintain balanced portfolio
-
self sufficient in cash
Limitations
BCG
matrix may not identify business with profitable market share and ignores
factors beyond market leader.
-
Low share business may also be profitable market share
-
relative to one (market leader/competition) other factors that determine
success
· GE PORTFOLIO MATRIX
Industry
attractiveness
Company’s
business strengths/Competitive position
Industry attractiveness - market growth rate, industry
profitability, size, pricing practices, opportunities/ threats
scale 1
- 5 Very unattractive to very attractive
Business strengths - Market share, technological
position, profitability, size, strengths & weakness
scale
1-5, 1- very weak, 5 - very strong
Product line - a letter, circle - area -
(size - scales) pie - market share
Identify performance group - current & projected
portfolio without any change in strategy
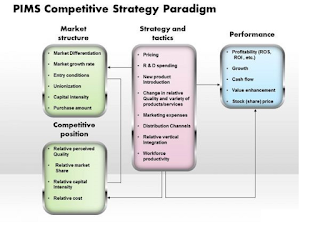
· Profit Impact of Market Strategy (PIMS)
The
Profit Impact of Market Strategies (PIMS) is a comprehensive, long-term study
of the performance of strategic business units (SBUs) in thousands of companies
in all major industries. The
Profit Impact of Market Strategy (PIMS) is a project that uses
empirical data to determine which business strategies make the difference
between success and failure. It is used to develop strategies for resource
allocation and marketing.
In the 1960s, General Electric came up with PIMS as an objective
approach to analyzing and learning from the great corporate performance. PIMS began as an internal project at General Electric (GE)
in 1960. Fred Borch, then a marketing vice-president and later the CEO,
initiated a project to quantify what factors led to success in GE´s diverse
businesses, from toasters to turbines, with sales already at $4 billion and
expected to more than double in a decade. (They did.) The original computer
model, which took five years to develop, was named PROM: Profitability Optimization Model. The data include information on markets, competitors,
quality, structure, environment and financial performance. Cross-sectional
regression analysis is a favored technique for verifying an hypothesis.
From 1972 to 1974 the on-going research was organized
as a project at Harvard Business School, giving birth to the Strategic Planning
Institute, SPI. At the beginning of 1974 the PIMS project was organized as an
independent non-profit organization, the Strategic Planning Institute. By
the middle 1980s the PIMS model had 400 items of information drawn from a
minimum of four years of operative and competitive information on 2,700
strategic business units (sbu´s). On the basis of this research, SPI could then
run scenarios for clients by entering different assumptions into the PIMS
computer model.
Since then, SPI researchers and consultants have continued working on the
development and application of PIMS data. According to the SPI, the PIMS
database is- "a collection of statistically documented experiences drawn
from thousands of businesses, designed to help understand what kinds of
strategies (e.g. quality, pricing, vertical integration, innovation,
advertising) work best in what kinds of business environments. The data
constitute a key resource for such critical management tasks as evaluating
business performance, analyzing new business opportunities, evaluating and
reality testing new strategies, and screening business portfolios.” The main
function of PIMS is to highlight the relationship between a business's key
strategic decisions and its results. Analyzed correctly, the data can help
managers gain a better understanding of their business environment, identify
critical factors in improving the position of their company, and develop
strategies that will enable them to create a sustainable advantage.
PIMS makes use of a unique library or database which keeps
expanding to this day and will continue to do so. The database comprises
cross-sectional and time-series data on approximately 4000 businesses collected
from more than 500 firms, big and small.
The information is built over a collection of 200 data items in
a standardized format, covering:
• The environment in
which the business operates
• The size of the target audience and the number of customers
• Market growth rates
• Channels of distribution
• Competitive position in the market
• Product/service price, quality, and costs involved
• Overall annual financial and operating performance
A key initial finding was that market share was a major driver to profitability. PIMS principles are taught in business schools, and the data are widely used in academic research. As a result, PIMS has influenced business strategy in companies around the world
The Strategic Planning Institute offers its PIMS model
(Profit Impact of Market Share) to clients to assist them in forming
strategy on the basis of empirically tested hypotheses. One runs split tests
and scenarios against the historical data in the PIMS database.
SPI
uses multi dimensional cross-sectional regression studies of profitability of
more than 4000 businesses. It then develops industry characteristics, Business
Average Profitability, and compares it with performances in the concerned
company
The most important factor to
emerge from the PIMS data is the link between profitability and relative market
share. PIMS found (and continues to find) a link between market share and the
return a business makes on its investment. The higher the market share – the
higher the return on investment. This is probably as a result of economies of
scale. Economies of scale due to increasing market share are particularly
evident in purchasing and the utilisation of fixed assets.
Profitability
is closely linked with market share.
A
10% improvement in profitability is linked with 5% improvement in Return on
Investment
When
to use PIMS
For small to
medium business operators, PIMS can be used to validate
your specific investment and expenditure strategies.
By analyzing the hordes of
evidenced data contained in the PIMS database, you can derive bulletproof
strategies to optimize the profitability of your business and encourage steady
growth.
Marketing managers can use
PIMS to understand their business environment and react to it accordingly. PIMS is used to develop and
test strategies for taking reliable financial measures.
Using its database, you
can identify critical strategic factors that will enable your business to
achieve a better, as well as a sustainable position in the market.
One can also:
• Determine the company’s future direction
• Recognize competitors and evaluate potential acquisitions
• Measure benchmark performance levels.
Strategic positioning is the chief determining factor
of business success.




No comments:
Post a Comment